Books for Depth of Knowledge Questioning
Jump straight to a section 👇
Depth of Knowledge definition
Depth of Knowledge wheel
DoK levels explained
Webb's Depth of Knowledge questions
Depth of Knowledge activities
What is Webb's Depth of Knowledge definition?

- In action, these context levels look different between subjects and age groups
- A student doesn't have to "master" learning and thinking at one level to progress to the next
- As a teacher, you can deliver different levels to your students through diverse activities, assessments and assignments
Depth of Knowledge wheel
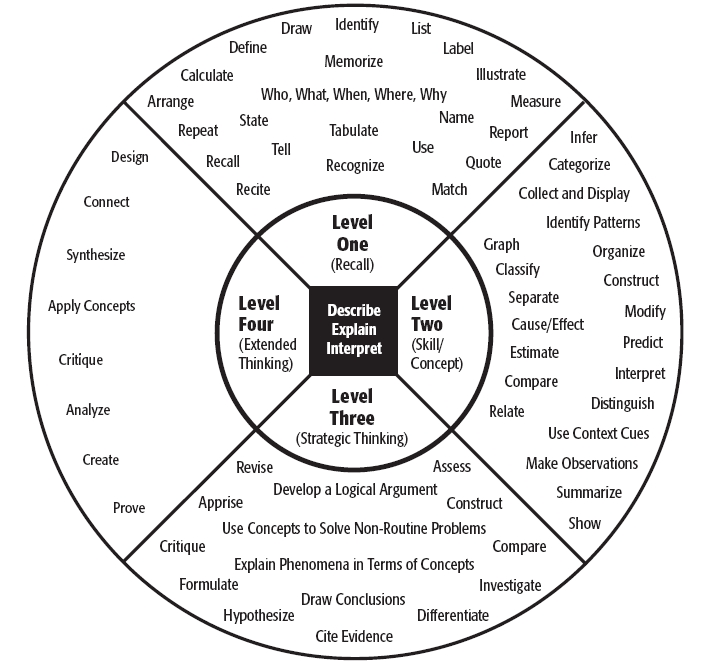
- Recall
- Knowledge application
- Strategic thinking
- Extended thinking
Understanding DoK levels 1 to 4

Recall: DoK level 1
The first Depth of Knowledge level is defined as recollection and reproduction. Rooted in simple exercises and procedures, students must remember facts, terms and formulas. There is little to no need for extended processing, as there aren't opportunities to "solve" anything. A student will or will not know the answer.Application: DoK level 2
The second Depth of Knowledge level is defined as knowledge application. Students must choose the appropriate route to correctly solve a question, making decisions and completing distinct steps along the way. For example, as opposed to reciting a math fact, they may have to solve a multi-step equation. To successfully do so, they may have to apply information in a different way or scenario than they learned it.Strategic thinking: DoK level 3
 The third Depth of Knowledge level is defined as strategic thinking. Students must face problems and scenarios that are more abstract than those in the previous level. Often, there may be different correct steps and answers. For example, writing an essay based on a defined topic can lead students in unique directions. As a result, they'll likely reach dissimilar conclusions.
The third Depth of Knowledge level is defined as strategic thinking. Students must face problems and scenarios that are more abstract than those in the previous level. Often, there may be different correct steps and answers. For example, writing an essay based on a defined topic can lead students in unique directions. As a result, they'll likely reach dissimilar conclusions. Critical thinking: DoK level 4
The fourth Depth of Knowledge level is defined as extended critical thinking. Students will get a mental workout. To complete a given challenge, they must typically gather information from different sources and disciplines. These challenges -- such as problem-based learning activities -- are usually linked to real-world problems without clear solutions, requiring students to justify their ideas and address counterpoints. As a result, students must critically think over relatively-long periods of time.Webb's Depth of Knowledge questions for every level

1st level Depth of Knowledge question stems
Asking specific questions can launch activities, exercises and assessments that only require recollection and reproduction. For example:| Recollection | Reproduction |
| When did ____ happen? | What is the formula for ____? |
| Who discovered ____? | How would you write ____? |
| Can you identify ____? | How would you describe ____? |
| What would you include on a list about ____? | How can you find the meaning of ____? |
2nd level Depth of Knowledge question stems
Like the first Depth of Knowledge level, you can ask specific questions to launch exercises that build skills and understandings of concepts. To get students in the proper mindset, ask:| Concept Reinforcing | Skill Building |
| What steps are needed to prove your answer for ____? | Can you demonstrate the steps to determine ____? |
| How would you estimate ____? | Using the concept of ____, can you solve ____? |
| Can you explain, in your own words, how ____ impacted ____? | Using the method of ____, can you explain how ____ impacted ____? |
3rd level Depth of Knowledge question stems
Question stems that promote strategic thinking include:| Strategic Thinking |
| How would you test ____? |
| What would happen if ____? Why? |
| Can you predict the outcome of ___? How? |
| What conclusions can you draw from ____? |
| What facts would you use to support the argument that ____? |
| What is your interpretation of ____? Support your theory or ideas. |
| Explain and justify the single best answer to this open question: ____? |
4th level Depth of Knowledge question stems
To encourage continuous strategic thinking, questions must be open-ended. This requires students to independently research and -- in the spirit of interdisciplinary learning -- fuse information from different classes and subjects. Some examples include:| Extended Critical Thinking |
| What information can you find and use to support your idea about ____? |
| Follow the scientific method to design and conduct an experiment, using ____. |
| Write and defend a thesis, forming your conclusion based on at least __ number of sources. |
| Apply information from one source to another source in a different subject. Develop an argument about the overarching topic. |
| From this list of topics I provide, pick one you know nothing about. Research the topic using at least __ number of sources. |
DoK questions for math
Adaptive and curriculum-aligned, Prodigy Math Game delivers questions that reflect Webb's DoK levels one to three.
Depth of Knowledge activities for any subject

Level 1 DoK
Despite a question's simplicity, you can still provide your class with many activities, having them finish a range of products. Depending on the question's purpose, students can:- Paraphrase a passage or chapter of a book
- Outline and re-iterate the main points of a recent lesson
- Complete a quiz or series of questions that only requires fact recall or fluency
- Make a timeline that maps historical or storybook events in relation to each other
- Deliver a short presentation to classmates that doesn't require independent research
Level 2 DoK
Requiring deeper thought than recollection and reproduction, there are many activities that stop just short of the third Depth of Knowledge level. Using questions as starting points, your class can:- Write blog, diary or journal entries
- Review texts in pairs or small groups
- Complete isolated, multi-step calculations
- Synthesize an explanation of a complex concept
- Create mind maps that show relationships between topics
- Design a physical model to demonstrate a scientific concept or historical event
Level 3 DoK
Activities and products associated with the above questions shouldn't inherently involve long-term research or drawing ideas from different subjects. That would extend into the final Depth of Knowledge level. Keeping this in mind, third-level activities include:- Writing an essay
- Composing venn diagrams
- Exploring a research question
- Delivering a persuasive speech
- Preparing and participating in a debate
- Completing complex equations related to real-world problems
Level 4 DoK
Activities that require these longer periods of critical thought lend themselves to high school or older elementary students. But, with a few changes, you can offer similar activities to younger pupils. For example, students can work in small groups to form and test hypotheses under in-class supervision. They can also:- Debate on one side of a contentious issue
- Partner or group with other students to complete a cross-subject research report and presentation
- Apply lessons from different subjects to pinpoint a problem's underlying issues, subsequently solving it
Additional Depth of Knowledge questioning strategies to apply in the classroom

| Listing and reviewing activities | At week's end, list each exercise you had your students do. Then, categorize them into the four Depth of Knowledge levels. This lets you reflect on how you structure your lessons, helping you target underrepresented thinking levels in upcoming classes. |
| Asking "Why?" | If you spend too much time on the first level, ask "why?" more . This challenges students to think about the facts and concepts they're recalling and reproducing. For example, if you're teaching how to make a slideshow, ask students why they think it is or isn't a viable supplement to presentations. |
| Allowing students to influence lesson structure | You know a lesson's essential questions, but you may not know how each student would best approach them. So, once per week or month as a higher-order thinking activity, allow students to brainstorm the lesson's hypothetical structure. Take their suggestions to deliver the ideal lesson the next day or week. This is a key element of experiential learning activities. |
| Switching, freely, between levels | There's a common misconception about applying Webb's theory. That is, students must grow proficient in one level before reaching the next. Such falsehoods are counterproductive. An engaging third-level task can, for example, help students build skills aligned with the first and second levels. Plus, dwelling on a level can dull your class. |
Final thoughts about Webb's Depth of Knowledge and DoK levels
Whether you see it as basic or complex, effectively applying Depth of Knowledge theory in your classroom takes practice. Using the questions, examples, activities and strategies in this guide should help you consistently craft engaging lessons that vary in cognitive effort. The content of these lessons will differ based on grade and subject. So, don't be skeptical if a colleague's strategic thinking exercises have little in common with yours. It's likely a sign of properly recognizing your students' distinct learning needs and styles.Join over 1.5 million teachers benefitting from Prodigy's Depth of Knowledge power. 👇
Books for Depth of Knowledge Questioning
Source: https://www.prodigygame.com/main-en/blog/webbs-depth-of-knowledge-dok/